API 6D Terms, Definitions, Acronyms, Abbreviations, Symbols, and Units
3 Terms, Definitions, Acronyms, Abbreviations, Symbols, and Units
3.1 Terms and Definitions
For the purposes of this document, the following definitions apply
3.1.1
assembly
Association of multiple parts/components into a finished product, including as a minimum, installation of all pressure-containing and pressure-controlling parts needed to ensure conformance to applicable pressure testing requirements
3.1.2
axial valve
Valve with a cylindrical closure member that moves on an axis parallel to the direction of flow
NOTE See Figure B.1 for a representative configuration for an axial on–off valve (provided for illustration purposes only),
3.1.3
bidirectional seat
Valve seat designed to seal against pressure source in either direction
3.1.4
bidirectional valve
Valve designed for blocking the flow in either direction
3.1.5
bleed (verb)
To drain or vent
3.1.6
block and bleed valve
BB
Valve with at least one seating surface that, in the closed position, provides a seal against pressure from one end of the valve with the body vented
3.1.7
block valve
Axial, ball, gate or plug valve that blocks flow when in the closed position
NOTE Valves may be either single seated or double seated or either bidirectional or unidirectional.
3.1.8
breakaway thrust
breakaway torque
Maximum thrust or torque required to operate a valve at maximum pressure differential
3.1.9
by agreement
Required understanding attained between the manufacturer and the purchaser needed for a given action to be completed.
NOTE If agreement is not reached, the associated action cannot be completed.
3.1.10
casting (noun)
Object at or near finished shape obtained by solidification of a fluid substance in a mold
NOTE Components made by hot isostatic pressing may not be identified as castings
3.1.11
closure member
Part of a valve, such as a ball, clapper, disc, gate, or plug, positioned in the flow stream to permit or prevent flow
NOTE Earlier editions of API 6D referred to this as an “obturator”.
3.1.12
design review and verification
Process of examining the result of design and development output to determine conformity with specified requirements
NOTE Design verification activities can include one or more of the following (this is not an all-inclusive list):
a) confirming the accuracy of design results through the performance of alternative calculations,
b) review of design output documents independent of activities of design and development,
c) comparing new designs to similar proven designs.
3.1.13
design validation
Process of proving a design by testing to demonstrate conformity of the product to design requirements
NOTE Design validation can include one or more of the following (this is not an all-inclusive list):
a) prototype tests,
b) functional and/or operational tests of production products,
c) tests specified by industry standards and/or regulatory requirements,
d) field performance tests and reviews.
3.1.14
double block and bleed valve
DBB
Valve with two or more seating surfaces that, in the closed position, provides a seal against pressure from both ends of the valve with a means of venting/bleeding the cavity between the seating surfaces
NOTE This valve does not provide positive double isolation when only one side is under pressure (see 3.1.15)
3.1.15
double isolation and bleed valve
DIB
Valve with two or more seating surfaces, each of which, in the closed position, provides a seal against pressure from a single source, with a means of venting/bleeding the cavity between the seating surfaces
NOTE This feature can be provided in one direction or in both directions.
3.1.16
downstream
Side of the valve where there would be no pressure or a lower pressure
NOTE 1 Where the valve is bidirectional, this reference may change sides.
NOTE 2 The term does not refer to flow direction.
3.1.17
drive train
All parts of a valve drive between the operator (but not including the operator) and the closure member that transmit or react to loads
3.1.18
flow coefficient
CV
Volumetric flow rate of water at a temperature between 40 ° F (5 °C) and 104 ° F (40 °C) passing through a valve and resulting in a pressure loss of 14.5 psi (0.1 MPa; 1 bar)
NOTE Kv is related to the flow coefficient Cv, expressed in USC units of U.S. gallons per minute at 60 °F (15.6 °C) resulting in a 1 psi pressure drop as given by Equation (1):
Kv = Cv /1.156 (1)
3.1.19
hand-wheel
Wheel used to manually operate a valve requiring multiple turns consisting of a rim connected to a hub (for example, by spokes)
3.1.20
locking device
Part or an arrangement of parts for securing a valve in the open and/or closed position
3.1.21
major weld repair
Any cavity prepared for repair welding that exceeds 20% of the part wall thickness or 1 in. depth, whichever is smaller or on the surface areas greater than 10 in.2 (64.5 cm2) or a through wall leak during any pressure testing
3.1.22
manufacturer
Organization that satisfies the requirements of this specification for activities that cannot be outsourced (3.1.29).
NOTE See 4.6.1 for activities that may be outsourced.
3.1.23
maximum allowable operating pressure
MAOP
Maximum pressure at which the valve is permitted to operate, at a specified temperature, as defined by ASME B16.34 Table 2
3.1.24
maximum allowable stem torque/thrust
MAST
Maximum torque /thrust that can be applied to the valve drive train without risk of damage, as defined by the valve manufacturer
3.1.25
maximum pressure differential
MPD
Maximum difference between the upstream and downstream pressure across the closure member at which the closure member may be operated.
3.1.26
nominal [diameter] size
DN
Numerical designation of size (in millimeters) that is common to components in piping systems
3.1.27
nominal pipe size
NPS
Numerical designation of size (in inches) that is common to components in piping systems
3.1.28
operator
Device (or assembly) for opening or closing a valve that includes an actuator, gearbox, and direct drive devices
NOTE 1 A manual operator can be a wrench (lever) or hand-wheel with or without a gearbox.
NOTE 2 An operator can bean electric, hydraulic, or gas device bolted or otherwise attached to the valve for powered opening and closing of the valve.
3.1.29
outsourced
Function, activity, or process that is performed by an external supplier on behalf of the manufacturer
3.1.30
packing gland
Components used to compress/retain the stem packing
3.1.31
piggability
Capability of a valve to permit the unrestricted passage of a pig
3.1.32
pipe pup
transition piece
Pipe or forged material that is welded to the valve
NOTE Pipe pups may be used to prevent valve-seal damage from girth welding or matching of valve material to pipeline strength
properties, or to provide a valve end matching the pipeline dimensions.
3.1.33
position indicator
Device to show the position of the valve closure member
3.1.34
pressure balance hole
Hole in the closure member that provides pressure balance between the valve bore and valve cavity only when in the open position, to avoid the cavity pressure being lower than the flow bore
3.1.35
pressure boundary bolting
Threaded fastener used to assemble pressure-containing parts
EXAMPLE Pressure boundary bolting can include studs, nuts, bolts, and cap screws.
3.1.36
pressure class
Numerical designation as defined in ASME Standard B16.34, which also defines the pressure and temperature rating for the end connector material of the valve.
NOTE The ASME rating class (pressure rating designation) is the word “Class,” followed by a dimensionless number (the designation for pressure–temperature ratings), for example: Class 150, Class 300, etc.
3.1.37
pressure-containing parts
Parts identified in 5.1.2 whose failure to function as intended results in a release of contained fluid into the environment
NOTE Pressure-containing parts do not include bolting (see Section 8).
3.1.38
pressure-controlling parts
Parts identified in 5.1.3 intended to allow or prevent the flow of fluids
3.1.39
receiving verification
Inward goods that are received at the manufacturer and identified as in conformance with the manufacturer’s purchase order requirements
3.1.40
remanufacturer
Organization performing disassembly, reassembly, and testing of a valve with or without replacement of parts that includes machining, welding, heat-treating, and/or other manufacturing operations, to maintain conformance to this specification.
NOTE Replacement of the body is not permitted.
3.1.41
repairer
Organization performing disassembly, reassembly, and testing of a valve with or without replacement of parts that does not include machining, welding, and heat-treating, other manufacturing operations, or replacement of bodies to maintain conformance to this specification.
NOTE Repair processes can include buffing, polishing, deburring, and other minimal removal processes.
3.1.42
sealing surface
Contact surface of dynamic or static seals within the valve shell, excluding end connector sealing surfaces that mate with other equipment.
EXAMPLES Sealing surface examples include the stem, seat, cover/bonnet seals and backseat.
3.1.43
seating surfaces
Contact surfaces of the closure member and seat that ensure valve sealing
3.1.44
self-relieving seat
Valve seat designed to relieve pressure in the valve cavity
NOTE Depending upon valve type, the pressure may be relieved to the pressure source or the low-pressure side.
3.1.45
shaft
Part that supports the closure member on a check valve and may or may not pass through the pressure boundary
3.1.46
shell test
Test of the assembled pressure-containing parts
3.1.47
stem
Part that drives the closure member and passes through the pressure boundary
3.1.48
stem extension assembly
Non-pressure containing assembly consisting of the stem extension and the stem extension housing
3.1.49
temperature, maximum operating
Upper temperature limit for product continuous operating service conditions
NOTE The maximum operating temperature may be limited by pressure.
3.1.50
temperature, minimum operating
Lower temperature limit for product continuous operating service conditions
NOTE The minimum operating temperature may be limited by pressure.
3.1.51
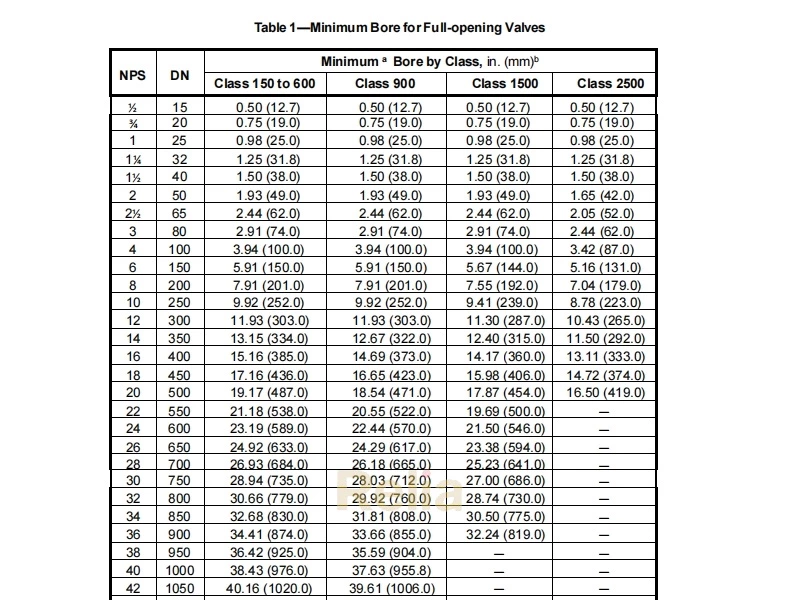
through-conduit valve
Valve with an unobstructed and continuous cylindrical opening
3.1.52
unidirectional seat
Valve seat designed to seal the pressure source in one direction only
3.1.53
unidirectional valve
Valve designed for blocking the flow in one direction only
3.1.54
unless otherwise agreed
Allowable modification of the requirements of this specification when the manufacturer and purchaser are in agreement
NOTE Modification of the requirements of this specification is permitted only for those clauses that include this term. If no modification agreement is identified between the manufacturer and purchaser, then the applicable clause is satisfied as stated.
3.1.55
upstream
Side of the valve where the pressure is retained.
NOTE 1 Where the valve is bidirectional, this reference may change sides.
NOTE 2 The term does not refer to flow direction.
3.1.56
visible leakage
Leakage of test fluid observed during a pressure test, either through direct observation or with the use of video equipment
NOTE Leakage may be observed through or past a pressure boundary or at an interface.
3.2 Acronyms and Abbreviations
For the purposes of this document, the following acronyms and abbreviations apply.
AWP ambient working pressure
ACCP ASNT Central Certification Program
API American Petroleum Institute
ASNT American Society for Nondestructive Testing
ASME American Society for Mechanical Engineers
ASTM American Society for Testing and Materials
AWS American Welding Society
BB block and bleed
BM base metal
BPVC boiler and pressure vessel code BSL bolting specification level
BTC break-to-close
BTO break-to-open
CE carbon equivalent
DBB double block and bleed
DIB double isolation and bleed
DN nominal size
DN nominal size
DPE double piston effect
ETC end–to–close
ETO end–to–open
HAZ heat-affected zone
HBW Brinell hardness, tungsten ball indenter
HRC Rockwell C hardness
ID Inner/Inside Diameter
ISO International Standards Organization
MAOP maximum allowable operating pressure
MAST maximum allowable stem torque/thrust
MPD maximum pressure differential
MSS Manufacturers Standardization Society
MT magnetic-particle testing
NDE nondestructive examination
NACE National Association of Corrosion Engineers
NORM Naturally Occurring Radioactive Material
NPS nominal pipe size
OD Outer/Outside Diameter
OEM original equipment manufacturer
PMI positive material identification
PQR (weld) procedure qualification record
PT penetrant testing
PWHT post-weld heat treatment
QSL quality specification level
QSL quality specification level
RT radiographic testing
RTC run–to–close
RTO run–to–open
SAE Society of Automotive Engineers
SMYS specified minimum yield strength
SPE single piston effect
SWL safe working limit
TC test coupon
TDI total dial indicator
TUS thermal uniformity survey
UT ultrasonic testing
VT visual testing
WM weld metal
WPS weld procedure specification
WPQ welder performance qualification
3.3 Symbols and Units
For the purposes of this document, the following symbols and units apply.
Cv flow coefficient in USC units
Kv flow coefficient in metric units
ppm part per million (mass)
Sm design stress intensity value
Sy [specified minimum] yield strength
t thickness